VVT Timing System
Reasonably select the timing of air distribution to ensure the best inflation efficiency η v. It is a very important technical problem to improve engine performance. By analyzing the working principle of internal combustion engine, it is not difficult to draw a conclusion that in the four periods of opening and closing of intake and exhaust valves, the change of late closing angle of intake valve affects the inflation efficiency η V has the greatest impact. Effect of late closing angle change of intake valve on inflation efficiency η The relationship between v and engine power can be further illustrated in Figure 1.
Each inflation efficiency in η The v curve reflects the inflation efficiency at a certain timing η V as a function of speed. If the late closing angle is 40 °, the inflation efficiency η V is the highest value at the rotating speed of about 1800r/min, which indicates that the inertia of air flow can be best used to inflate at this rotating speed. When the speed is higher than this speed, the air flow inertia increases, so that part of the gas that could have used the air flow inertia to enter the cylinder is closed outside the cylinder. In addition, when the speed rises, the flow resistance increases, so the inflation efficiency is increased η V decreases. When the speed is lower than this speed, the inertia of air flow decreases, and some fresh air may be pushed back to the intake pipe at the beginning of the compression stroke, thus the inflation efficiency η V also decreases.
Different inflation efficiency η The v curve reflects the inflation efficiency under different valve timing η V as a function of speed. Different intake late closing angles and inflation efficiency η The speed corresponding to the maximum value of v curve is different, and the late closing angle generally increases, which is similar to the inflation efficiency η The speed corresponding to the maximum value of v curve also increases. Compared with the charging efficiency hv curve with a late closing angle of 40 ° and a late closing angle of 60 °, the speed corresponding to the maximum value of the curve is 1800 r/min and 2200 r/min respectively. As the rotational speed increases, the airflow speed increases, and the large late closing angle can make full use of the high-speed airflow inertia to increase inflation.
Changing the late closing angle of intake air can change the inflation efficiency η The trend of v curve changing with the speed to adjust the engine torque curve to meet different operating requirements. However, to be more precise, increase the late closing angle of the intake valve and the inflation efficiency at high speed η The increase of v is beneficial to the increase of maximum power, but unfavorable to the low speed and medium speed performance. Reducing the late closing angle of intake air can prevent the gas from being pushed back into the intake pipe, which is conducive to increasing the maximum torque, but reducing the maximum power. Therefore, the ideal valve timing should be adjusted timely according to the working conditions of the engine, and it should have a certain degree of flexibility. Obviously, for the traditional cam tappet valve mechanism, it is difficult to meet the above requirements due to the inability to make corresponding adjustments in the work, which limits the further improvement of the engine performance.
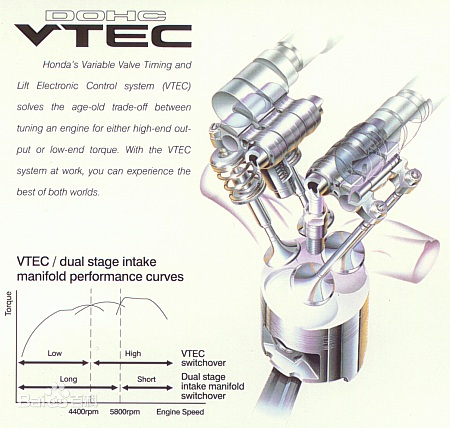
VTEC Timing System
The full name of VTEC system is the variable valve timing and lift electronic control system, which is Honda's proprietary technology. It can properly adjust the valve timing and valve lift according to the changes of engine speed, load, water temperature and other operating parameters, so that the engine can achieve the highest efficiency at high and low speeds. In the VTEC system, there are three cam surfaces on the inlet camshaft, respectively jacking the three rocker arms on the rocker arm shaft. When the engine is at low speed or low load, there is no connection between the three rocker arms. The left and right rocker arms jack the two inlet valves respectively, so that they have different timing and lift to form the effect of air squeezing. At this time, the high speed rocker arm in the middle does not push the valve, but only makes invalid movement on the rocker arm shaft. When the speed is increasing, the sensors of the engine will send the monitored load, speed, speed, water temperature and other parameters to the computer, and the computer will analyze and process these information. When it is required to change to high-speed mode, the computer sends a signal to open the VTEC solenoid valve, so that the pressure oil enters the jacking piston in the rocker shaft, so that the three rocker arms are connected into one, so that both valves operate in high-speed mode. When the engine speed decreases to meet the valve timing and needs to be changed again, the computer sends a signal again to open the VTEC solenoid valve pressure head to drain the pressure oil, and the valve returns to the low speed working mode again.
After the ordinary engine is manufactured, the valve timing and valve lift are fixed, which cannot meet the engine's demand for intake and exhaust at different speeds. Therefore, traditional engine designers always adopt a compromise scheme when considering the camshaft profile, considering both high speed and low speed. However, this comprehensive design scheme limits the performance of the engine to some extent, which is far from meeting the requirements of vehicle engines. Therefore, people hope to have such an engine, whose cam profile can adapt to any speed, and get the best valve timing no matter at high speed or low speed. Therefore, the variable valve timing control mechanism came into being. Among the variable valve timing control mechanisms, Honda's VTEC system is the most representative.
 Huzhou Sanjing Auto Parts Co., Ltd
Huzhou Sanjing Auto Parts Co., Ltd